CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing: Designing a Glyco-Optimized Pichia Pastoris for Cancer Immunotherapy
The past decades has seen the rapid development of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-associated protein 9(CRISPR-Cas9) in many sectors including in genomic engineering for strain development. CRISPR-Cas9 has emerged as powerful platforms for revolutionized genetic engineering by enabling precise, efficient and cost-effective genome editing1. Targeted mutation in CRISPR-Cas9 enabling the genome editing without introducing foreign DNA and generate non-transgenic which give more gain from public acceptance and regulatory approval.
Pichia Pastoris strain has been utilized in Biopharma industries in producing several drugs or therapeutics proteins products including cancer drugs2. One of the most challenging aspects of biomanufacturing is producing humanised drugs and proteins from Pichia Pastoris strain. In this study , CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing use as a scalpel to knock down precisely related genes in O-glycosylation pathway that adds sugar serine/thereonine residues on recombinant Anti-PD-L1 antibodies protein to produce more human compatible sugar (Figure 1).
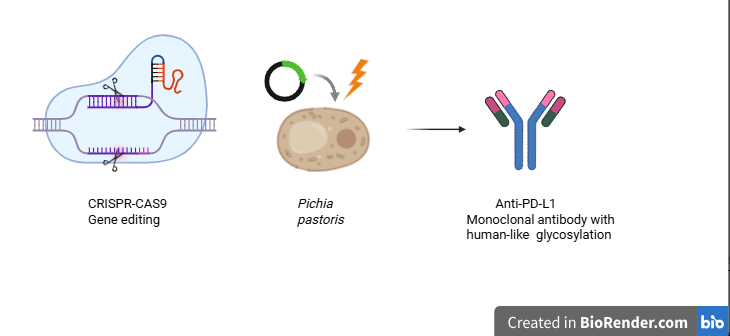
Illustration of Purpose of the project. Produced through Biorender Apps.
References:
- Gostimskaya I. (2022). CRISPR-Cas9: A History of Its Discovery and Ethical Considerations of Its Use in Genome Editing. Biochemistry. Biokhimiia, 87(8), 777–788. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297922080090.
- Dudeja, C.; Mishra, A.; Ali, A.; Singh, P.P.; Jaiswal, A.K. Microbial Genome Editing with CRISPR–Cas9: Recent Advances and Emerging Applications Across Sectors. Fermentation2025, 11, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11070410
Author: Noorhamizah Binti Suhaimi
NanoBio4Can MSCA Co-Fund Fellow
Izmir Biomedicine and Genome Center (IBG)